

The entropy changes during phase transition notes provide comprehensive information about how entropy changes when there is a change in the phase. As the heat energy increases, it increases the kinetic energy, which breaks the intermolecular binding forces.

Hence, when there is an increase in heat and temperature, it increases the disorder of the molecules and increases the entropy. When there is a phase transition, the system releases or absorbs a large amount of energy per volume change. Hence, it is shown by the following equation:
Change in entropy free#
Gibbs free energy is the energy that is converted into the system at constant pressure and temperature. At thermodynamic equilibrium, when the phase transition occurs quasi–statistically, the total entropy change of the system and surroundings is zero.įree energy is the internal energy of a thermodynamic system that helps perform work.However, there is a decrease in the system’s entropy if the phase is towards lower internal energy, and it leads to the transition of the phase from gaseous or liquid to solid. The entropy changes during phase transition increase when there is melting of the phase as it leads to higher internal energy change.As there is an increase in the temperature, it increases the random movement of the molecules and hence increases the rate of entropy.Hence, the entropy will move toward zero when a phase is in perfect order.Įntropy changes during phase transition occur, and free energy changes As per the third law of thermodynamics, when the temperature of solid crystalline is at its absolute temperature, it increases the entropy to zero.According to the second law of thermodynamics, heat transfer into work takes place only at the expense of energy hence, there is a continuous surging of entropy level due to the transfer of heat into work.This is because the number of moles of gaseous products rises compared to the reactants. Hence, where there is a phase transition, it leads to a surge in the entropy. According to the first law of thermodynamics, energy cannot be destroyed nor created, but it can be changed from one form to another.The entropy changes during phase transition are thermodynamically shown as energy is transferred from one phase to another due to an increase in the random disorder. It helps establish the relationship between all forms of energy and how it is transferred from one form to another. Thermodynamics is an important branch of physics that helps show the relation between heat and various forms of energy. Entropy in terms of ThermodynamicsĮntropy can be explained thermodynamically and is associated majorly with three laws of thermodynamics. However, when there is a change in the state from gas to solid, it decreases the level of entropy. As there is a change in the state from solid to gaseous, it gradually increases the level of entropy. Hence, it is found that there are entropy changes during the phase transition from solid to gaseous and vice versa. As the level of randomness is higher, it has the highest entropy compared to all the types of molecules. Gases readily disperse and hence have a high level of randomness or disorganisation of molecules.However, as it is not tightly packed like a solid, it has a higher level of entropy than a solid. The liquid is free-flowing but does not readily disperse.The level of disorder in the solid is low and therefore has the lowest entropy. Solid has a regular arrangement of the molecules, and hence it is tightly packed.Each state has its entropy, and it varies based on the type of phase, and the level of entropy changes based on the phase. The molecules exist in solid, liquid, and gaseous states.

Why do entropy changes during phase transition occur? The topic includes comprehensive information and entropy changes during phase transition notes. The heat transfer is reversible at a constant phase transition temperature.
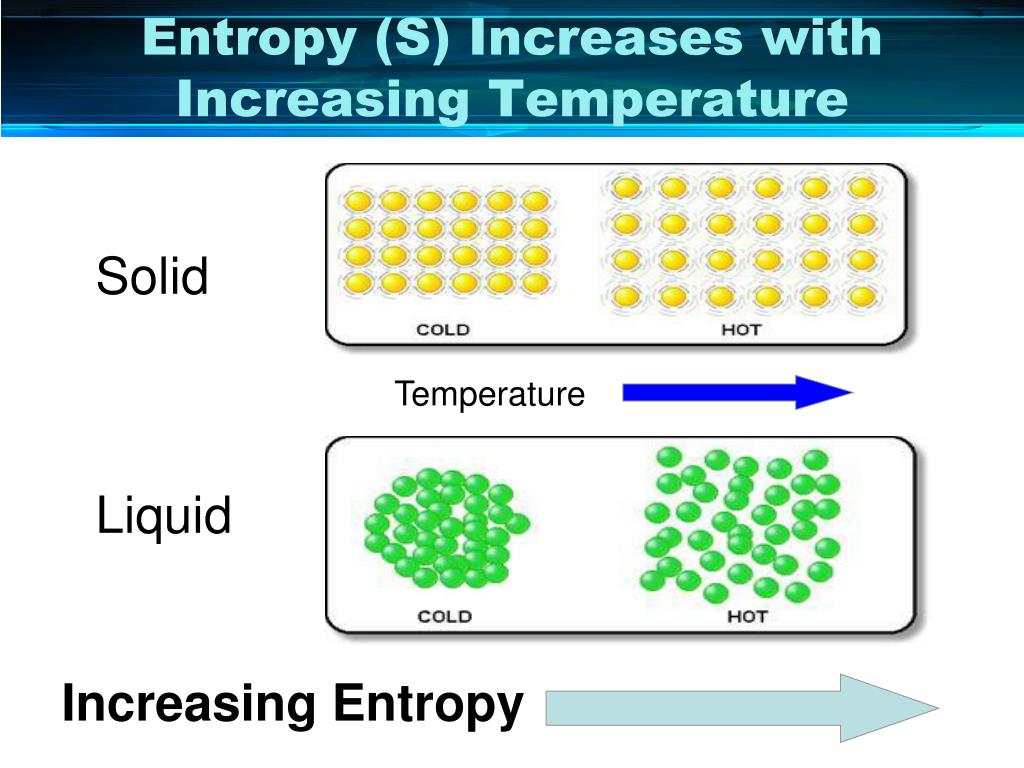
During the phase transition, the temperature remaining constant impacts the entropy. When there is a change in the phase, it leads to a change in the randomness or organisation of the molecules and hence impacts the overall entropy. However, entropy changes during phase transition decrease when the change lowers the internal energy. It is an important scientific concept that helps calculate the state of disorder or uncertainty-the entropy changes during phase transition increase when a phase transitions towards higher internal energy. Entropy measures the state of randomness or a measure of disorder.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
